Homework 1
Due Date: April 15, 1999
Points: 100
Short-Answer Questions
These can be answered in a sentence or two,
and are intended to reinforce important points.
- (3 points) What is multiprogramming? (Tanenbaum, problem 1.2)
- (6 points) Name the layers of the THE operating system,
and briefly describe the function of each.
- (4 points) Why was time-sharing not widespread on second generation
computers? (Tanenbaum, problem 1.5)
Long-Answer Questions
These questions require some thought and longer answers than
the short-answer questions. They are intended to have you use
the concepts discussed in class, to be sure you understand them
and can work with them.
- (14 points) Protecting the resident monitor is crucial to a
correctly operating computer system. Providing this protection is the
reason behind multiple mode operation, memory protection, and the
timer. To allow maximum flexibility, however, we would also like to
place minimal constraints upon the user. The following is a list of
operations which are normally protected. What is the minimal set of
instructions which must be protected?
- Change to user mode.
- Change to monitor mode.
- Read from monitor memory.
- Write into monitor memory.
- Instruction fetch from monitor memory.
- Turn on timer interrupt.
- Turn off timer interrupt.
- (15 points) Some early computers protected their operating
systems against destruction by placing it in memory locations from
which all programs (including the operating system itself) could read,
but into which no program could write. What problem does this
protection scheme create?
- (20 points) Three conventions for communicating the
arguments of a service call to the kernel are to place them on a stack,
in registers, or right after the call. What are the advantages and
disadvantages of these three strategies?
- (18 points) The classical batch processing system completely
ignores the cost of increased waiting time for users. Consider a single
batch characterized by the following parameters:
| M | average mounting time |
| T | average service time per job |
| N | number of jobs |
| S | unit price of service time |
| W | unit price of waiting time per user |
Show that the optimal batch size minimizing the cost of service time and
waiting time per user within a single batch is
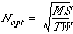 .
.
- (20 points) In the example of virtual machines, with a
compiler above an operating system above two levels of virtualizing
kernel, how many privileged instructions would be executed at each
level if the instruction executed by the compiler can be emulated
without use of privileged instructions by the operating system?
Extra Credit
- (5 points) In class I used CPU utilization to illustrate how
successive generations made more effective use of the computer. How
meaningful is the CPU utilization to the users? What other question (or
questions) would users like to know the answer to?
- (10 points) In MINIX, why is the CHROOT system call limited
to the super-user? (Hint: think about protection problems.) (Tanenbaum,
Problem 1.14)
 Send email to
cs150@csif.cs.ucdavis.edu.
Send email to
cs150@csif.cs.ucdavis.edu.
Department of Computer Science
University of California at Davis
Davis, CA 95616-8562
Page last modified on 4/7/99
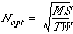 .
.
 Send email to
cs150@csif.cs.ucdavis.edu.
Send email to
cs150@csif.cs.ucdavis.edu.